Google Guidelines to Image SEO | How to Make Images Rank on SERP
Whether websites or blogs, you would have noticed relatable images everywhere.
Images are information conveyed visually that enhances the understandability of content if prepared well. Self-explicable images appeal to visitors to visit the source, i.e., website, thus improving web traffic.
On-page SEO strategy remains incomplete without image optimization (Image SEO) as images boost content visibility and generate more organic traffic.
Image SEO allows the search crawler to discover more information about an image and enhances its reach by getting visibility in Google’s Image Search.
All in all, creating SEO-friendly images for blogs or websites would get you high ranking, visibility, improved page load times, and tons of traffic. Image optimization has been in action for a long, but the ever-changing rules and algorithms of search engines make optimization a bit challenging.
Let’s dive deep to find effective and easy ways to do image optimization.
Choose the Right Image Format
JPEG, PNG, and GIF are three of the most commonly used image file types. Choosing the best file type for your website is of utmost value as it decides on the speed of the site. The images are believed to slow down the speed of the site. So what’s the point of adding images?
As explained above, the image holds the supreme ability to attract potential customers and crawlers. For a faster user experience, you can simply incorporate responsive image techniques and the latest image optimization. Check the speed of your site using the PageSpeed Insights tool.
Websites don’t do with one or two images but require plenty of them to describe the purpose of the site. High-quality and right size image compression would help you attain the desired speed for your site. Color variation and complex shading go with JPEG; the image format can be compressed to get expected results.
While PNG turns out to be a high-resolution file format offering high transparency and color support, it may slow down the size if not compressed well. The third one is GIF; it is a moving image and is best to show animation.
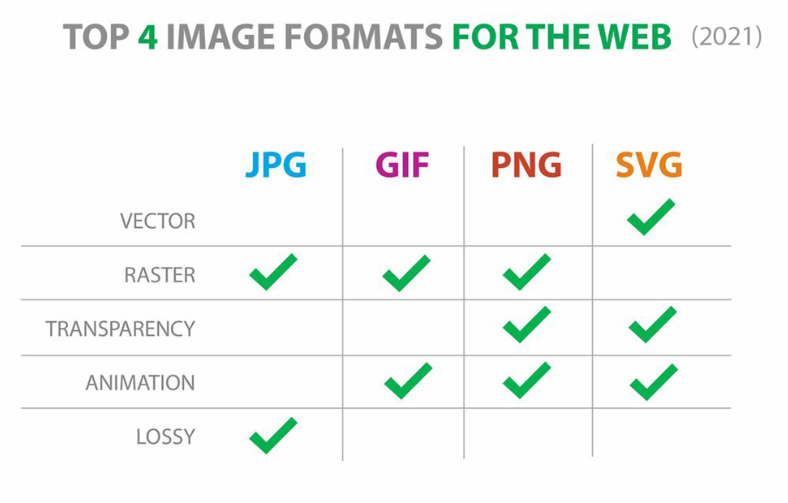
JPEG – Reduced Quality +Reduced Size (for photos)
PNG - Better Quality + Larger Size (for custom graphics, line drawings, text, logos and screenshots)
GIF - Animated Raster Graphics File; Good Quality + Considerable Size (for animated graphics)
The better the quality, the higher will be its appeal to the viewers. The reduced the size, the faster will be its loading speed. So, be careful to pick one. Use attractive thumbnails to get more clicks.
Resize the Image
The size of the image plays an important part. The large image size can slow down the loading speed of the site, which eventually affects the user experience. Compressing the image size can help you upkeep the loading speed.
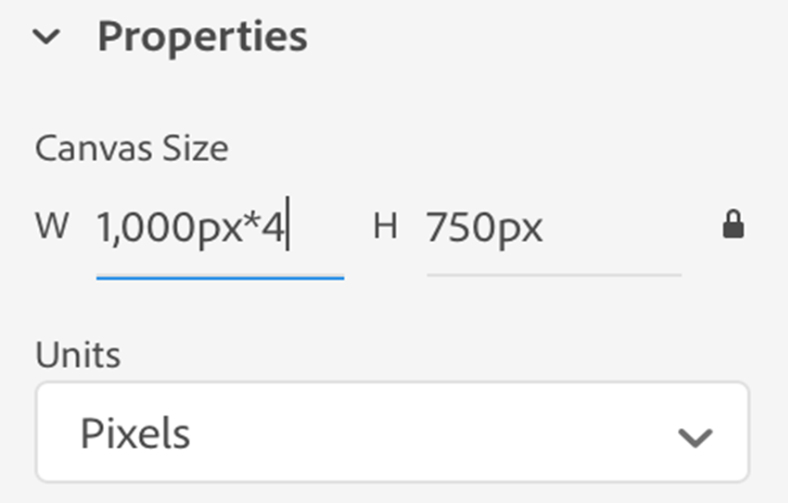
Have you noticed the white space margins on either side of the website? These margins are marked for the maximum limit of blog content, i.e., 720px. If it exceeds the limit, the browser will resize the image, but it will take the required loading time to load the image even if it displays it at 720px.
The higher the pixels, the bigger the file size. There are tools that can help you resize the image as per the requirement (both in bulk and individually).
In the case of AMP and PWA, predefining the image dimensions in the source code would allow the resizing of the image before CSS loads to help you improve the user experience. Undefined images and content shifts affect the Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) score, so make sure that you allocate the width and height of the image accordingly.
Optimize for Mobile First Images

With more and more users shifting to mobile phones to access sites and blogs, it’s a must to optimize the site for mobile-first indexing. This makes the image responsive for all screen sizes. No matter what's the device size, the content will scale accordingly for both desktop and mobile.
For instance: You uploaded an image of 720px. When a user tries to access a website with a small screen display size (320px). The image will show up the same for both, but to load the image with 720px, it will take extra bandwidth and servers. It will affect the loading speed and user experience as well.
For this, we can use the HTML code “srcset and sizes attributes”
<img src="image.jpg" srcset="image-medium.jpg 1000w, image-large.jpg 2000w">
Check if your site is mobile-friendly or not using the Mobile-Friendly Test tool.
Use descriptive and SEO-Friendly Alt-Text
Alt attribute is the description of an image. It describes the content in an image file.
Alt attributes are also called alternative text that is displayed when the browser fails to render images. These attributes add relevance to the image and are a vital part of on-page SEO.
Google has proposed some guiding principles for the creation of SEO friendly Alt Tags, which says:
"Alt text (text that describes an image improves accessibility for people who can't see images on web pages, including users who use screen readers or have low-bandwidth connections".
"Google uses alt text along with computer vision algorithms and the contents of the page to understand the subject matter of the image. Also, alt text in images is useful as anchor text if you decide to use an image as a link".
"When choosing alt text, focus on creating useful, information-rich content that uses keywords appropriately and is in the context of the content of the page. Avoid filling alt attributes with keywords (keyword stuffing) as it results in a negative user experience and may cause your site to be seen as spam”.
Alt tags are known to improve accessibility, topical relevance, and image rank in Google images. These alt tags can also be used as anchor text. Be concise in length, use effective and self-explanatory words and avoid keyword redundancy and stuffing.
Add Structured Data
- Adding structured data fields to an image would validate to Google that an image is licensable. Structured data helps Google to identify and classify the content of a web page and generate required information in a standardized form. Here is the go-to guide to help you build, add, test and release structured data.
- Add acquireLicensePage property and other required properties. Check JSON-LD structured data to know where to put structured data on the page.
- Walkthrough general and specific structured data guidelines.
- Use the Rich Results Test to justify your code.
- Use the URL Inspection tool to gain insight into how Google reads your page. Remove all unnecessary files and folders from robots.txt files, the no-index tag, or login requirements to ensure that Google can access your pages. If things look fine, invite crawlers to go through your web page.
- Submit a sitemap to let Google follow every possible change. Use Search Console Sitemap API to automate the process.
Write Appropriate Page Title & Description
Have you ever noticed that Google images come with a title and snippet to explain the image? Apart from being a ranking factor, it guides visitors to click on the image that goes with their search query. The process of the information displayed on Google images is fully automated as it takes into account the information generated from references on the web and the content of the page, including descriptive information in the title and Meta tags. Learn how to form good titles and snippets in search results.
Conclusion
While Google adds value to the image over content and drafts certain guidelines to be followed for optimal ranking, following these guidelines can be a hard nut to crack. Image optimization is not a piece of cake. Image SEO is growing more complex with voice search coming into trend. In case you need any help, contact us.
Recent Posts
Why are ERP solutions important in the education sector?
Which is the best ERP solution provider company?
How do we select the right ERP solution for our businesses?
9 Most In-Demand Programming Languages for 2024
Best Time to Post on Social Media – 2024 Guide
Why You Should Consider Semantic HTML for SEO
All Categories
- Bing
- Blockchain
- Blog
- Branding
- Case Study
- Content Marketing
- Conversion Rate Optimization
- Cryptocurrency
- Digital Currency
- Digital Marketing
- Email Marketing
- ERP Solutions
- Facebook Marketing
- Google Ads
- Google Updates
- Graphic Designing
- Hire Developers
- Image SEO
- Influencer Marketing
- IT
- Local SEO
- Machine Learning
- Mobile Application Development
- Pay Per Click
- Pinterest SEO
- Podcast Hosting
- React JS
- Reddit & Quora
- Search Engine Optimization
- SEO Copywriting
- Social Media Marketing
- Software
- Software Development
- Technology
- UX and UI
- Web Designs
- Web Hosting
- Website Development
- Website Redesigning
- YouTube SEO








